Measuring Combustion Efficiency in Atmospheric Boilers and Furnaces

Combustion eficiency is a measurement of how well any given fuel is being burned and converted into useful energy (e.g.: heat). The calculations are based on three MAJOR factors:
- Chemistry of the burned fuel (e.g. propane, natural gas, oil, etc)
- The CO2 percentage by volume after the combustion process
- The NET temperature between the stack gas and the primary air being used
How to calculate the efficiency of a boiler
Since the net temperature is a KEY parameter in combustion efficiency calculations, this will explain how the ΔT is measured. When testing most common atmospheric boilers, furnaces, and water heaters, our Combustion Analyzers use its own built-in internal temperature sensor to measure the Room’s actual Ambient Temperature (Ta) because the room air is used as the primary air being fed into the system for combustion. When the probe is placed in the stack, the analyzer measures the Flue Stack Temperature (Tg) simultaneously with the ambient air. As listed above, the combustion Eficiency is calculated by the net differential temperature of the primary ambient room temperature and the Flue Stack Temp.
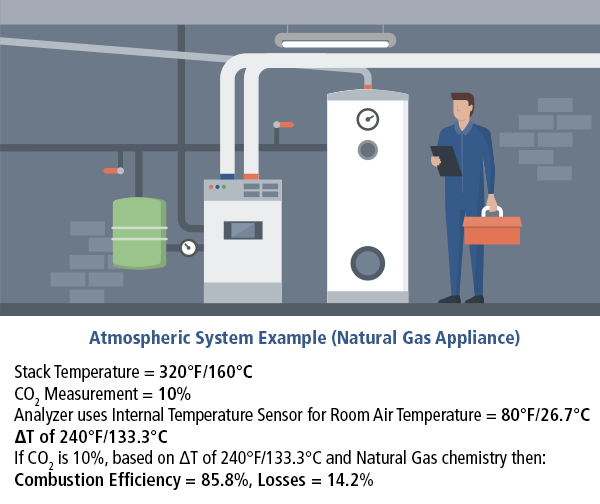
See this example:
320 °F in the stack - the ambient 80°F = ΔT of 240°F
Our combustion analyzer automatically takes this ΔT calculation which is then also automatically combined with the analyzer’s CO2 reading and the chemistry of the type of fuel being burned (natural gas, oil, etc.) to fully calculate, display and record the appliance’s overall Combustion Efficiency.




Add new comment