Adverse Health Effects of Elevated Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Levels in Homes

The Sources Of NO2 In Homes
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) is a colorless, odorless gas that is commonly emitted from home heating elements such as gas, wood, oil, kerosene, and coal burning appliances, including stoves, space heaters, water heaters, furnaces, boilers and fireplaces. Gas engines, including those found in cars and home generators, also emit NO2 which can also contribute to increased levels of this toxic gas. Elevated NO2 levels caused by improper home ventilation can cause eye, nose and throat irritation, and can contribute to a variety of respiratory problems including shortness of breath and chronic bronchitis.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, young children are especially susceptible to NO2 overexposure, and are more likely to develop respiratory infections or asthma when exposed to even low levels of NO2. (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency).1
OSHA Exposure Limits and Health Effects of Nitrogen Dioxide
| Concentration | Effects |
| < 0.1 PPM Good | Should have minimal health effects or occupant complaints |
| 0.1 to < 5 PPM Marginal | Could produce some negative health effects among vulnerable populations, including asthmatics and others with respiratory issues |
| > 5 PPM Critical | Likely to cause serious health effects or discomfort among all populations |
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)2, the permissible exposure limit for NO2 in homes and offices should not exceed 5 ppm (9 mg/m3). However, NO2 levels as low as 0.1 ppm have been shown to cause respiratory discomfort in vulnerable populations such as asthmatics. The accumulation of potentially toxic gases in homes, such as NO2, VOC’s and formaldehyde, is of increased concern due to the current movement of “tightening buildings” for the sake of energy efficiency. An over tightened home without a mechanism to exchange stale indoor air for fresh outdoor air may lead to unhealthy levels of NO2 and other gases which are typically emitted from common residential elements. A thorough understanding of the indoor air quality of the home, including possible toxic gas accumulation, is an important step towards increasing the health, safety and comfort of occupants.
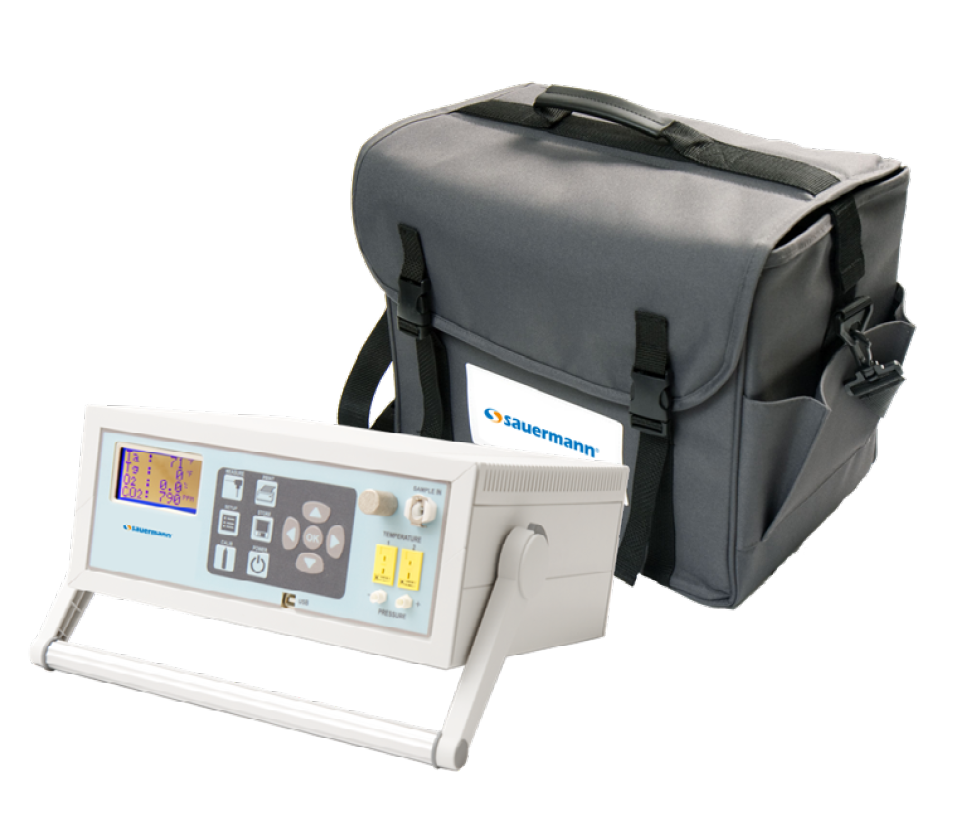
NO2 Monitoring Solution
The measurement of the concentration of NO2 commonly found in indoor environments can be performed using the Sauermann Si-AQ EXPERT IAQ monitor. This specialized monitoring instrument utilizes technology that allows air quality analysts, environmental safety companies, laboratory technicians, etc., to quickly and accurately monitor the levels of NO2 present in the breathing environments of homes, office buildings, laboratories, or industrial facilities.
The Si-AQ EXPERT includes software with real-time continuous data logging, wireless Bluetooth® compatibility and can be customized to monitor up to 11 different parameters relevant to indoor air quality.
¹ Asthma Triggers: Gain Control Nitrogen Dioxide. United States Environmental Protection Agency.
² Nitrogen Dioxide: General Description. United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration.